Airports, hotels, cafés, even shopping malls, offer public charging points where you can boost your phone or laptop battery on the go.
They’ve been in the news after the FBI recently tweeted advice to stop using them. Crooks have figured out how to hijack USB ports to install malware and monitoring software onto devices as they charge.
The security risk of “juice jacking” was long thought to be more theoretical than real, but the tech needed to carry out an attack has gotten smaller and cheaper and easier to use. This means less sophisticated criminals are now turning their hand to it.
So how does it work?
The most common charging cables – USB-C and lightning – are dual-purpose. They have pins for charging and pins for data.
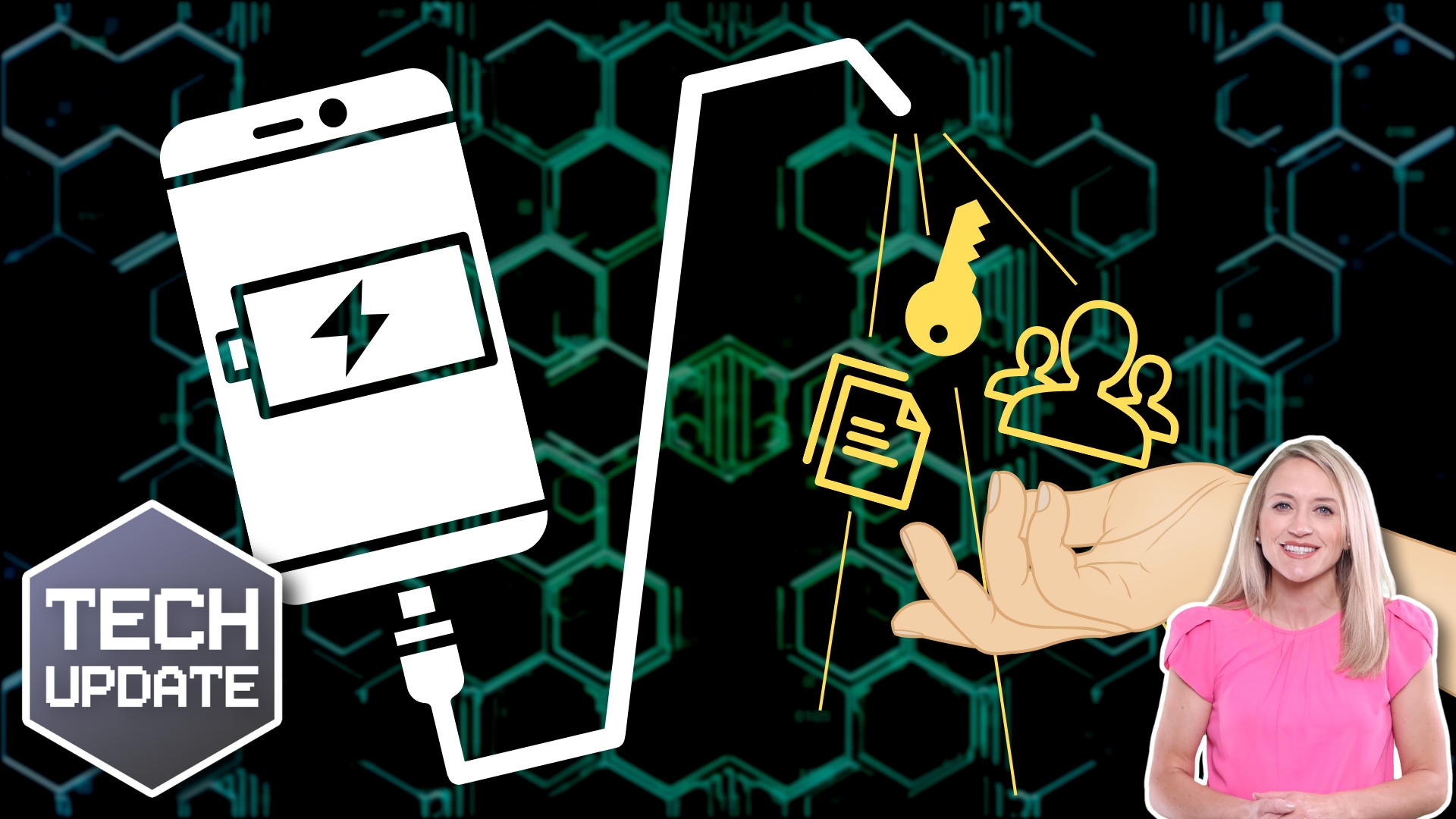
When you charge your device, you only use the charging pins. But a compromised charging port – or a cable that someone has left behind – could use both charging pins and data pins without you knowing.
When they use the data pins, criminals can install malware onto your device that gives them access to your credentials and other data. It’s a little like plugging your phone into someone else’s laptop.
To avoid the risk, the best solution is to always carry your own charger and cable, and plug it into a power outlet. If you have no choice but to use a public USB port, invest in something called a USB data blocker. This prevents data being transferred, but the device will still charge.
We help businesses stay secure and productive at the same time.
If we can help you, get in touch.
Published with permission from Your Tech Updates.